Ladakh
WELCOME TO Ladakh
Territory Overview
Leh
59,146 km2
274,000
Ladakhi
Popular
Geography and Tourist Attractions
Information about the state's tourist attractions, including popular destinations, events, and activities.
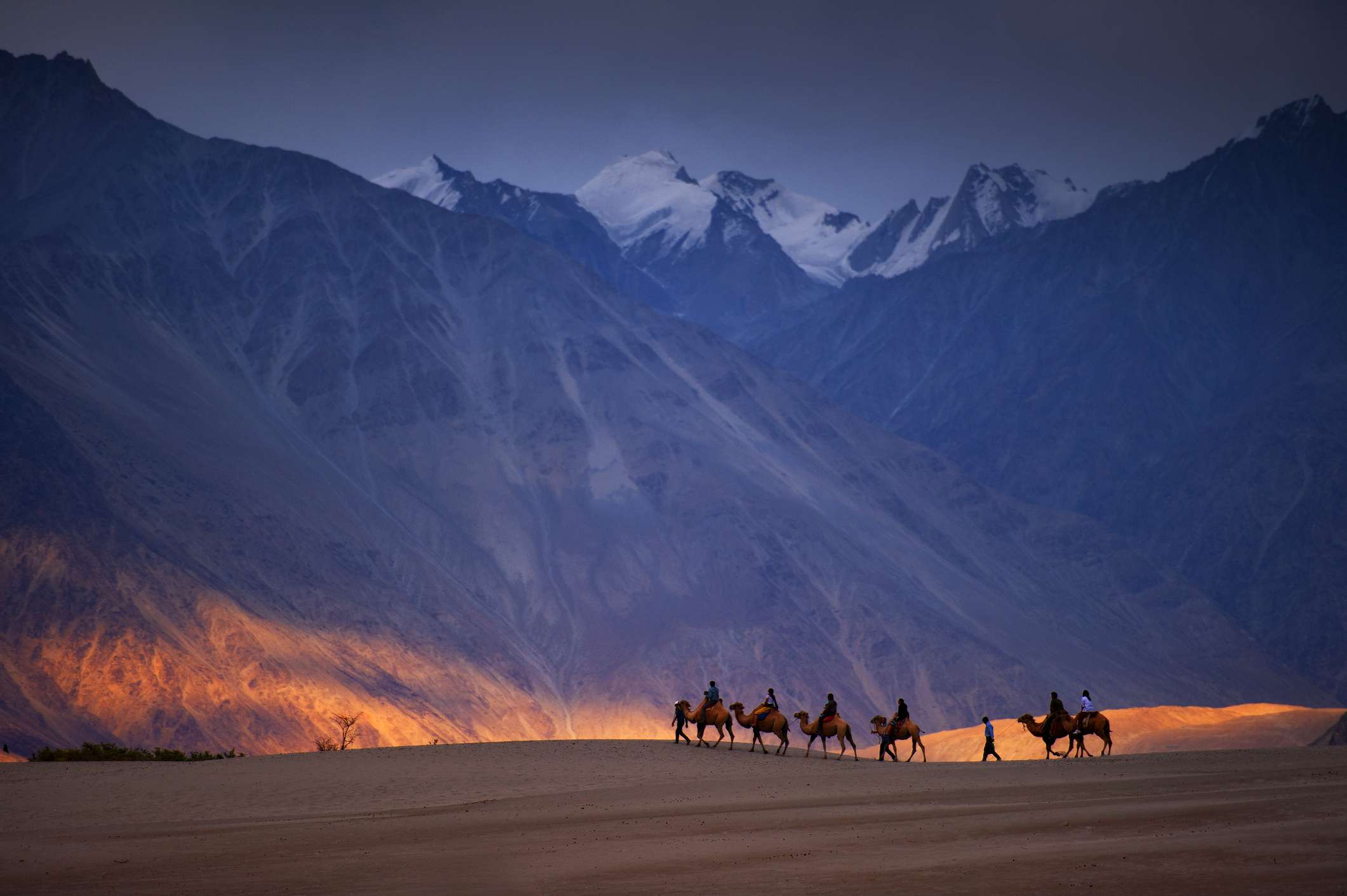

Nubra Valley
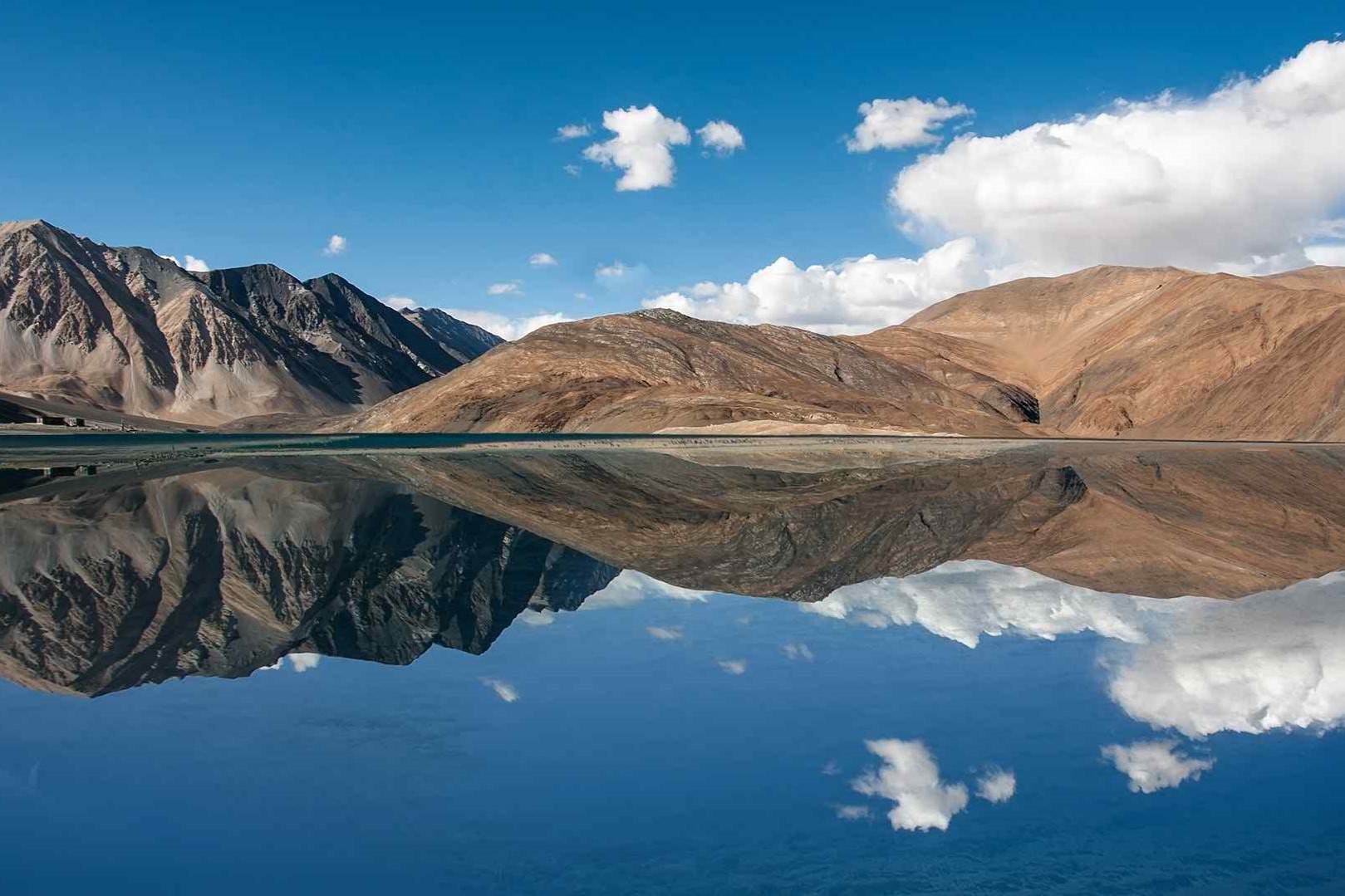

Pangong Tso
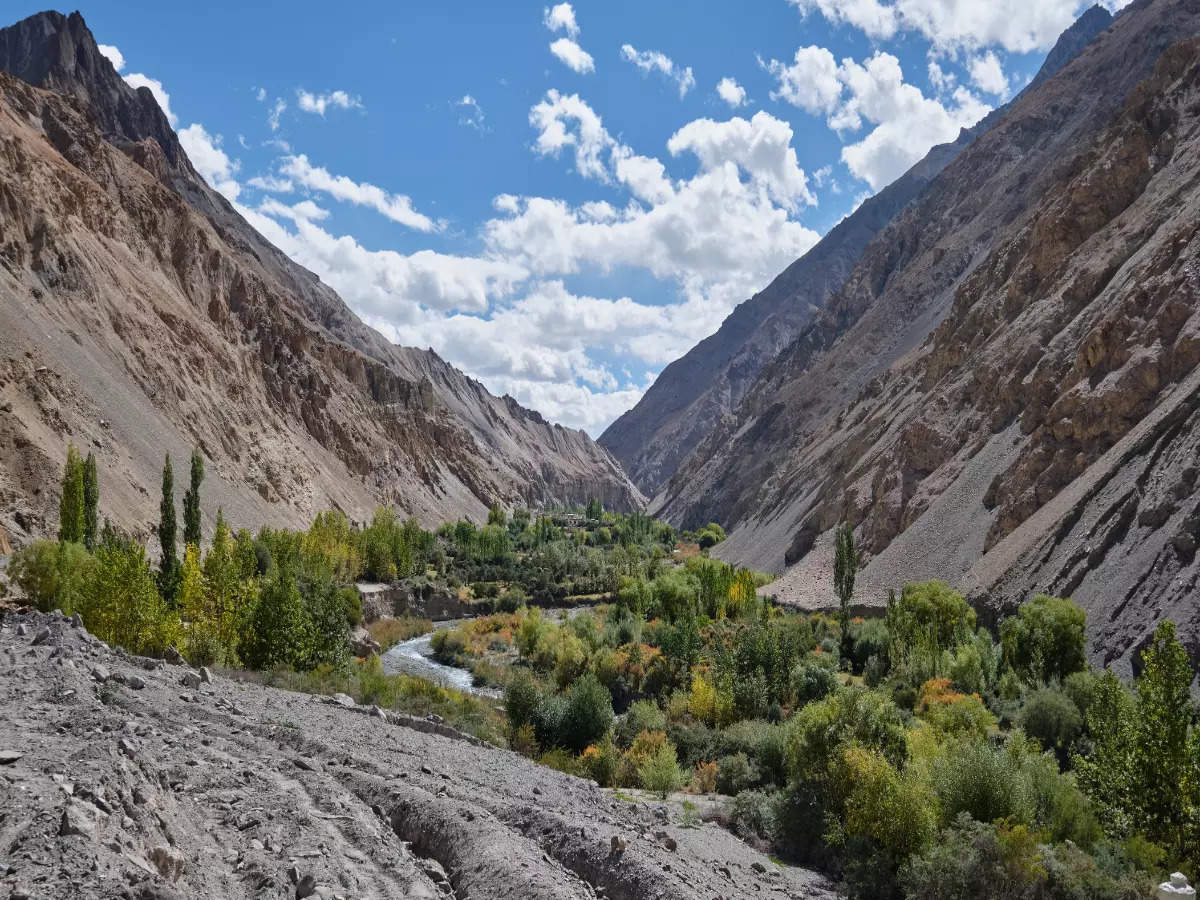

Hemis National Park
Political
Economy and Government
The economy of the Territory of Ladakh in India is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and handicrafts. Ladakh has a unique geographical location that presents both opportunities and challenges. The region is known for its production of barley, wheat, vegetables, and fruits. Animal husbandry, particularly rearing yaks, sheep, and goats, is also significant for the local economy.
In recent years, tourism has emerged as a vital sector, attracting a large number of domestic and international visitors. The picturesque landscapes, monasteries, and adventure activities like trekking and river rafting contribute to the tourism industry's growth. Efforts are being made to promote sustainable tourism and preserve the region's fragile ecosystem.
The government of Ladakh operates under the governance structure of a Union Territory. The Lieutenant Governor is the administrative head and is appointed by the President of India. Ladakh has its own legislative assembly, known as the Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LAHDC), which plays a significant role in local governance. The LAHDC is responsible for policy formulation and implementation of development programs in the region.
The central government of India provides financial support and guidance to the Ladakh administration for development initiatives. Efforts are being made to promote economic growth, improve infrastructure, and enhance the overall well-being of the people of Ladakh.

History
History and Culture
Ladakh, situated in the northernmost region of India, is a land steeped in rich history and vibrant culture. With its breathtaking landscapes, snow-capped peaks, and serene monasteries, Ladakh has captivated travelers for centuries.
Historically, Ladakh served as a significant crossroad on the ancient Silk Route, connecting India, Central Asia, and China. It was ruled by various dynasties, including the Tibetan Empire and the Kushan Empire, leaving behind a tapestry of cultural influences. The region's historical significance is evident in its majestic palaces, such as the Leh Palace, which stands as a testament to Ladakh's royal heritage.
Ladakh's culture is predominantly influenced by Tibetan Buddhism. The region is dotted with monasteries that showcase remarkable art, intricate murals, and sacred relics. Hemis Monastery, Thiksey Monastery, and Diskit Monastery are among the revered Buddhist sites, where colorful festivals like Hemis Tsechu attract both locals and visitors.
Ladakh's people, known as Ladakhis, have preserved their unique traditions and way of life. From their traditional attire, adorned with vibrant colors and intricate designs, to their warm hospitality, Ladakhis embody the essence of their culture.
Today, Ladakh's history and culture continue to thrive amidst modernization, making it a captivating destination where visitors can immerse themselves in a captivating blend of ancient traditions and awe-inspiring landscapes.
HOTELS
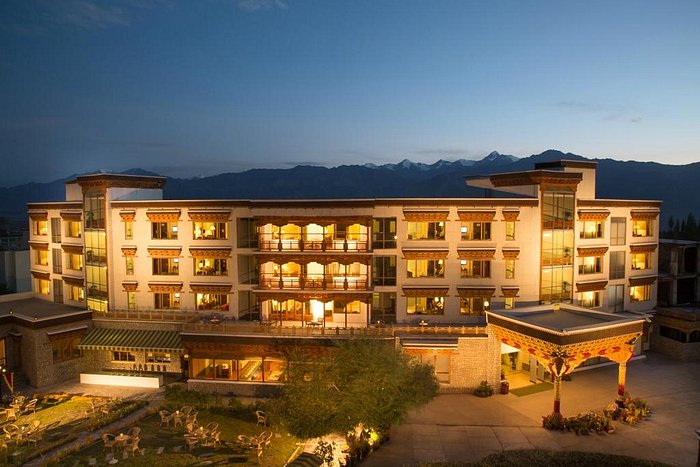

The Grand Dragon Ladakh
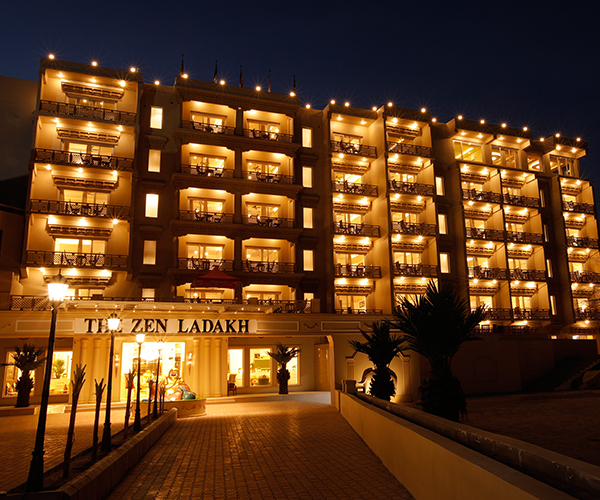

The Zen Ladakh
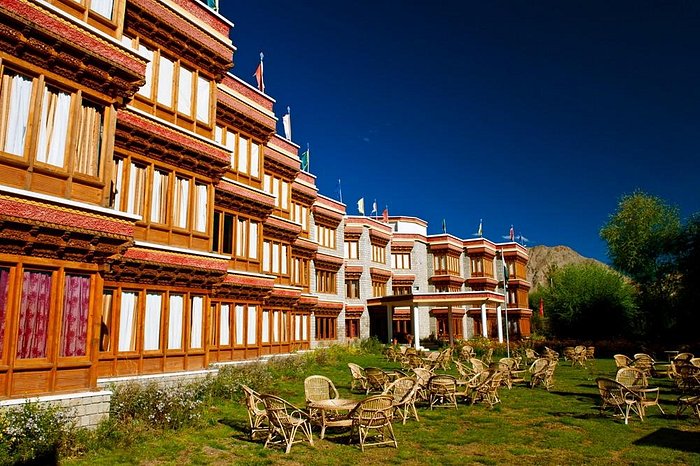

The Druk Ladakh
RESTAURANTS
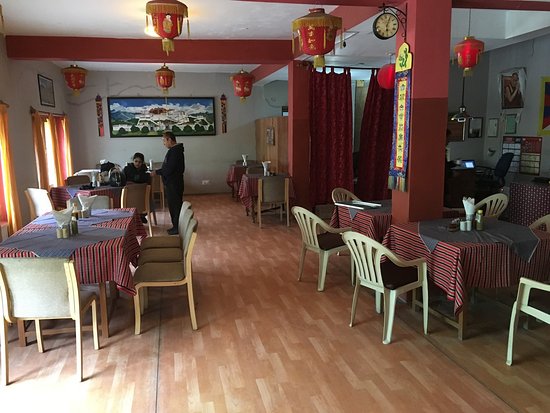

Tibetan Kitchen

The Apricot Tree Restaurant

